面试场景还原
面试官:在实际业务场景中,我们常常需要在海量数据(列如几十亿个数)中快速判断某个数是否存在。你有什么高效的解决方案吗?
面试者:对于这种海量数据查找问题,常规的HashMap或数据库查询在内存和性能上都会遇到瓶颈。我推荐使用布隆过滤器(Bloom Filter) 这种概率型数据结构,它能够在很小的内存占用下实现快速的存在性判断。
布隆过滤器原理
布隆过滤器是一个空间效率很高的概率型数据结构,它由一个很长的二进制向量和一系列随机映射函数组成。它的核心特性是:
- 可能存在(可能存在误判)
- 必定不存在(100%准确)
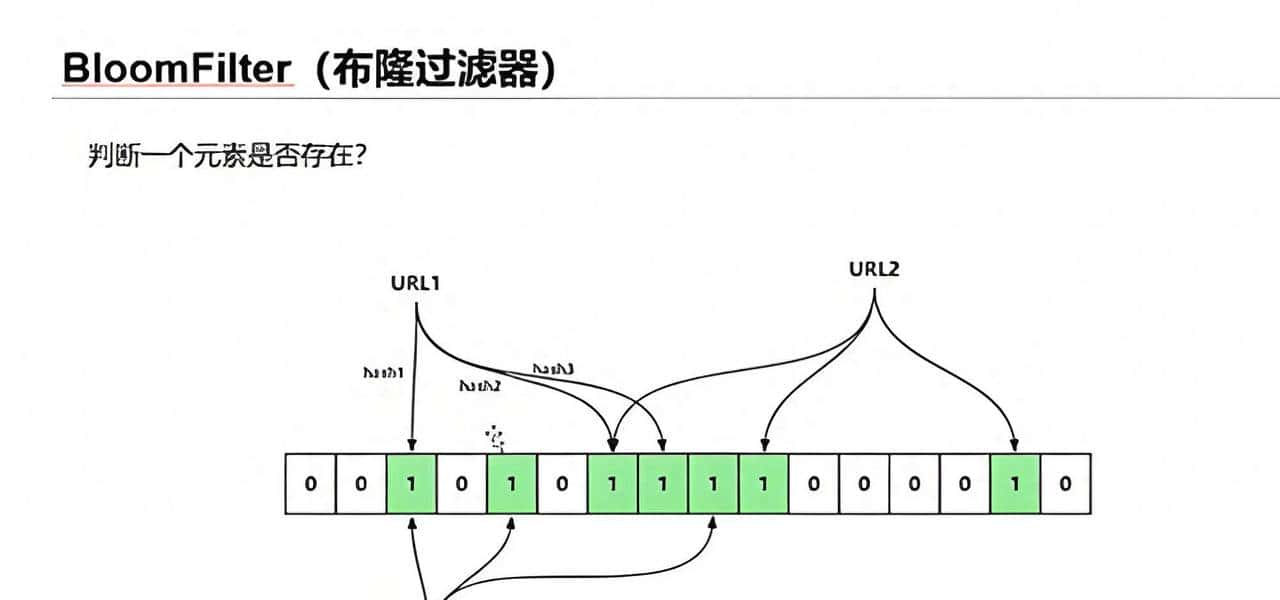
工作原理
- 初始化:创建一个长度为m的位数组,所有位初始化为0
- 添加元素:使用k个不同的哈希函数对元素进行哈希,将对应的位数组位置设为1
- 查询元素:使用同样的k个哈希函数计算位置,如果所有位置都为1,则元素可能存在;如果有任何一个位置为0,则元素必定不存在
布隆过滤器原理
Java实现布隆过滤器
import java.util.BitSet;
import java.util.function.Function;
/**
* 布隆过滤器实现
*/
public class BloomFilter<T> {
private final BitSet bitSet;
private final int bitSetSize;
private final int numHashFunctions;
private final Function<T, Integer>[] hashFunctions;
/**
* 构造布隆过滤器
* @param expectedInsertions 预期插入元素数量
* @param falsePositiveRate 期望的误判率
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public BloomFilter(int expectedInsertions, double falsePositiveRate) {
if (falsePositiveRate <= 0 || falsePositiveRate >= 1) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("误判率必须在0和1之间");
}
// 计算最优的位数组大小和哈希函数数量
this.bitSetSize = calculateBitSetSize(expectedInsertions, falsePositiveRate);
this.numHashFunctions = calculateNumHashFunctions(expectedInsertions, bitSetSize);
this.bitSet = new BitSet(bitSetSize);
// 初始化哈希函数
this.hashFunctions = new Function[numHashFunctions];
initializeHashFunctions();
}
/**
* 计算最优的位数组大小
*/
private int calculateBitSetSize(int n, double p) {
return (int) Math.ceil(-n * Math.log(p) / (Math.log(2) * Math.log(2)));
}
/**
* 计算最优的哈希函数数量
*/
private int calculateNumHashFunctions(int n, int m) {
return Math.max(1, (int) Math.round((double) m / n * Math.log(2)));
}
/**
* 初始化哈希函数
*/
private void initializeHashFunctions() {
for (int i = 0; i < numHashFunctions; i++) {
final int seed = i;
hashFunctions[i] = obj -> {
int hash = obj.hashCode();
// 使用不同的种子来创建不同的哈希函数
hash = hash ^ (seed * 0x5bd1e995);
hash = hash ^ (hash >>> 16);
hash = hash * 0x5bd1e995;
hash = hash ^ (hash >>> 13);
return Math.abs(hash % bitSetSize);
};
}
}
/**
* 添加元素
*/
public void add(T element) {
for (Function<T, Integer> hashFunction : hashFunctions) {
int position = hashFunction.apply(element);
bitSet.set(position);
}
}
/**
* 判断元素是否可能存在
* @return true: 可能存在; false: 必定不存在
*/
public boolean mightContain(T element) {
for (Function<T, Integer> hashFunction : hashFunctions) {
int position = hashFunction.apply(element);
if (!bitSet.get(position)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
/**
* 获取布隆过滤器的统计信息
*/
public void printStats() {
int setBits = bitSet.cardinality();
double utilization = (double) setBits / bitSetSize;
System.out.println("布隆过滤器统计信息:");
System.out.println("位数组大小: " + bitSetSize);
System.out.println("哈希函数数量: " + numHashFunctions);
System.out.println("已设置位数: " + setBits);
System.out.println("位数组利用率: " + String.format("%.2f%%", utilization * 100));
}
}性能测试与对比
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* 布隆过滤器性能测试
*/
public class BloomFilterBenchmark {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 测试参数
int totalElements = 10_000_000; // 1000万数据量
int testQueries = 100_000; // 10万次查询
double falsePositiveRate = 0.01; // 1%误判率
System.out.println("测试数据量: " + totalElements);
System.out.println("目标误判率: " + falsePositiveRate);
// 初始化布隆过滤器
BloomFilter<Integer> bloomFilter = new BloomFilter<>(totalElements, falsePositiveRate);
// 初始化对照组(HashMap)
HashSet<Integer> hashSet = new HashSet<>(totalElements);
// 生成测试数据
Random random = new Random(42);
int[] testData = new int[totalElements];
for (int i = 0; i < totalElements; i++) {
testData[i] = random.nextInt(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
// 测试布隆过滤器添加性能
long bloomStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int value : testData) {
bloomFilter.add(value);
}
long bloomAddTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - bloomStartTime;
// 测试HashMap添加性能
long hashSetStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int value : testData) {
hashSet.add(value);
}
long hashSetAddTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - hashSetStartTime;
// 测试查询性能
int[] queryData = new int[testQueries];
for (int i = 0; i < testQueries; i++) {
if (i % 2 == 0) {
// 一半查询存在的数据
queryData[i] = testData[random.nextInt(totalElements)];
} else {
// 一半查询不存在的数据
queryData[i] = random.nextInt(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
}
// 布隆过滤器查询测试
long bloomQueryStart = System.currentTimeMillis();
int bloomHits = 0;
for (int value : queryData) {
if (bloomFilter.mightContain(value)) {
bloomHits++;
}
}
long bloomQueryTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - bloomQueryStart;
// HashMap查询测试
long hashSetQueryStart = System.currentTimeMillis();
int hashSetHits = 0;
for (int value : queryData) {
if (hashSet.contains(value)) {
hashSetHits++;
}
}
long hashSetQueryTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - hashSetQueryStart;
// 计算误判率
int falsePositives = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < testQueries; i++) {
if (i % 2 != 0) { // 只检查不存在的数据
int value = queryData[i];
if (bloomFilter.mightContain(value) && !hashSet.contains(value)) {
falsePositives++;
}
}
}
double actualFalsePositiveRate = (double) falsePositives / (testQueries / 2);
// 输出结果
System.out.println("
性能对比结果:");
System.out.println("布隆过滤器 - 添加时间: " + bloomAddTime + "ms");
System.out.println("HashMap - 添加时间: " + hashSetAddTime + "ms");
System.out.println("布隆过滤器 - 查询时间: " + bloomQueryTime + "ms");
System.out.println("HashMap - 查询时间: " + hashSetQueryTime + "ms");
System.out.println("实际误判率: " + String.format("%.4f", actualFalsePositiveRate));
// 内存使用对比
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
runtime.gc();
long bloomMemory = runtime.totalMemory() - runtime.freeMemory();
bloomFilter.printStats();
}
}实际应用场景
1. 缓存穿透保护
/**
* 使用布隆过滤器防止缓存穿透
*/
public class CacheWithBloomFilter {
private final BloomFilter<String> bloomFilter;
private final Map<String, Object> cache;
public CacheWithBloomFilter(int expectedSize) {
this.bloomFilter = new BloomFilter<>(expectedSize, 0.01);
this.cache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
}
public Object get(String key) {
// 先检查布隆过滤器
if (!bloomFilter.mightContain(key)) {
return null; // 必定不存在,直接返回
}
// 可能存在,查询缓存
Object value = cache.get(key);
if (value == null) {
// 缓存穿透情况,可以在这里进行数据库查询
// 但布隆过滤器已经过滤了大部分不存在的key
}
return value;
}
public void put(String key, Object value) {
// 先添加到布隆过滤器
bloomFilter.add(key);
// 再放入缓存
cache.put(key, value);
}
}2. 分布式系统应用
/**
* 分布式布隆过滤器示例
*/
public class DistributedBloomFilter {
private final List<BloomFilter<String>> shards;
private final int numShards;
public DistributedBloomFilter(int totalCapacity, double falsePositiveRate, int numShards) {
this.numShards = numShards;
this.shards = new ArrayList<>(numShards);
int shardCapacity = totalCapacity / numShards;
for (int i = 0; i < numShards; i++) {
shards.add(new BloomFilter<>(shardCapacity, falsePositiveRate));
}
}
private int getShardIndex(String key) {
return Math.abs(key.hashCode()) % numShards;
}
public void add(String key) {
int shardIndex = getShardIndex(key);
shards.get(shardIndex).add(key);
}
public boolean mightContain(String key) {
int shardIndex = getShardIndex(key);
return shards.get(shardIndex).mightContain(key);
}
}优化提议
- 选择合适的哈希函数:使用MurmurHash、FNV等高质量哈希函数
- 动态扩容:当数据量超过预期时,可以创建新的布隆过滤器
- 计数布隆过滤器:支持删除操作,但需要更多空间
- 分层布隆过滤器:应对数据分布不均匀的情况
总结
布隆过滤器是处理海量数据存在性判断的利器,特别适合以下场景:
- 缓存穿透保护
- 爬虫URL去重
- 垃圾邮件过滤
- 数据库查询优化
虽然有必定的误判率,但在大多数业务场景中,这种概率是可接受的。通过合理配置参数,可以在内存占用和准确率之间找到最佳平衡点。
面试提议:在回答这类问题时,不仅要给出技术方案,还要结合实际业务场景,分析各种方案的优缺点,展示你的综合思考能力。
© 版权声明
文章版权归作者所有,未经允许请勿转载。
相关文章

暂无评论...