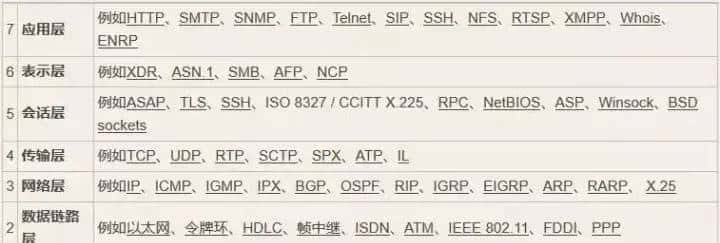
一、相对定位——relative
有偏移量(left、right、top、bottom)时,元素相对于自身进行偏移,元素不脱离文档流(在原位置还占有空间),不影响其他元素布局。
<style>
#one{
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
background: orangered;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
#two{
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
background: hotpink;
border: 1px solid #aaaa7f;
position: relative;
top: 10px;
opacity: 0.5;
}
#three{
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
background: skyblue;
border: 1px solid #5c5c5c;
}
</style>
<body>
<div id="one"></div>
<div id="two"></div>
<div id="three"></div>
</body>
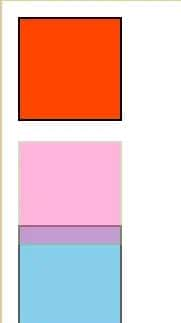
二、绝对定位——absolute
有祖先元素时,当祖先元素有了任一position(绝对、相对、固定),且子元素设置为绝对定位后,子元素相对于当前的祖先元素进行偏移;子元素会脱离文档流(后面的div会覆盖上来);绝对定位使内联元素支持宽高(块特征),使块元素的默认宽根据内容决定(内联特征)。
<style>
#father{
width: 250px;
height: 200px;
border: 1px solid #FFD47F;
position: relative;
}
#one{
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
background: orangered;
border: 1px solid #000;
position: absolute;
right: 20px;
top: 0px;
}
#two{
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
background: hotpink;
border: 1px solid #aaaa7f;
opacity: 0.5;
}
#three{
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
background: skyblue;
border: 1px solid #5c5c5c;
}
</style>
<body>
<div id="father">
<div id="one"></div>
<div id="two"></div>
<div id="three"></div>
</div>
</body>
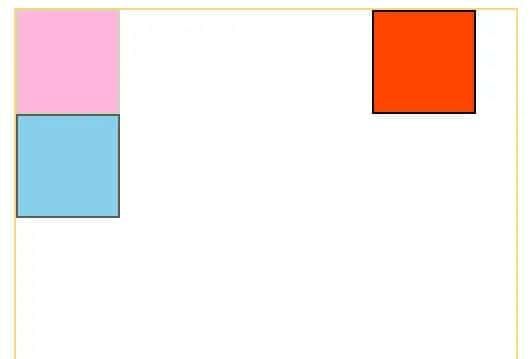
三、固定定位——fixed
使元素脱离文档流,使内联元素支持宽高,使块元素的默认宽根据内容决定;相对于整个浏览器窗口进行偏移,不受浏览器滚动条影响。

四、粘性定位——sticky
在指定位置,进行粘性操作。
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1gt4y1m7Eo
© 版权声明
文章版权归作者所有,未经允许请勿转载。
相关文章

暂无评论...